Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS):
In this condition, the cells lining the milk ducts (the channels in the breast that carry milk to the nipple) are cancerous, but stay contained within the ducts without growing through into the surrounding breast tissue. DCIS may affect just one area of the breast, but can be more widespread and affect different areas at the same time. Sometimes, DCIS may be described as Pre-Cancerous, Pre-Invasive, Non-Invasive, or intraductal cancer.
Important Definitions:
Lobules:Spherical-shaped sacs in the breast that produce milk.
Duct:
A pathway in the breast through which milk passes from the lobules to the nipple.
Lobular carcinoma In Situ (LCIS)
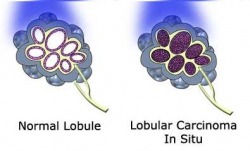
LCIS has the potential to become invasive carcinoma, and so is treated as an early form of breast cancer. In lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS, the image to the right), the lobular cells have developed the ability to multiply out of control - one of the characteristics of cancer. The cancerous cells have not yet spread beyond the lining of the lobule.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is thought to be a 'pre-cancerous' condition. This means is not true cancer, because the cells, while abnormal, have not developed the ability to spread beyond the lobules of the breast. Lobular carcinoma in situ is still an important finding, however, because a woman with LCIS is at higher risk of developing true invasive breast cancer than unaffected women.
Back To What Is Breast Cancer
